Navigation by alphabet
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y ZIndex
Pool Boiling
DOI 10.1615/hedhme.a.000192
2.7 BOILING AND EVAPORATION
2.7.2 Pool boiling
J.G. Collier and V. Wadekar
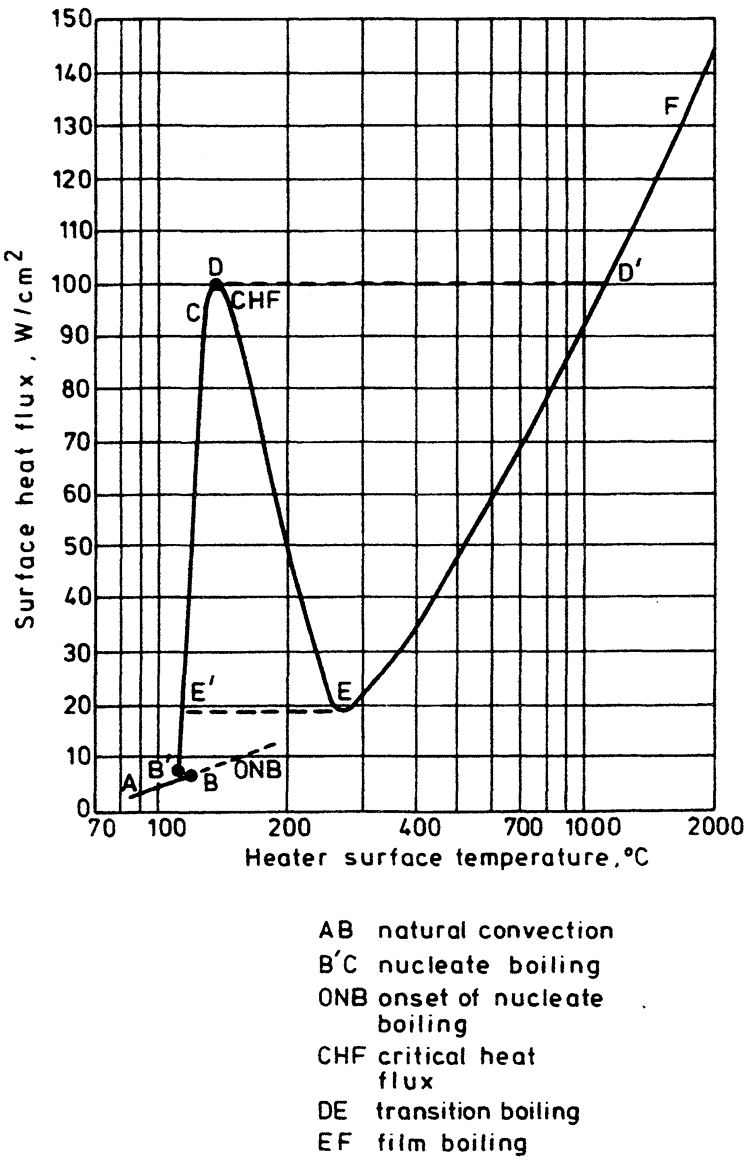
Pool boiling is defined as boiling from a heated surface submerged in a large volume of stagnant liquid. This liquid may be at its boiling point, in which case the term saturated pool boiling is employed, or below its boiling point, when the term subcooled pool boilingis used. The results of investigations into heat transfer rates in pool boiling are usually plotted on a graph of surface heat flux (q̇) against heater wall surface temperature (Tw) — the boiling curve. Such a curve for water boiling at atmospheric pressure is shown diagrammatically in Figure 1. An alternative presentation might use the wall superheat (Tw – Tsat) rather than the wall temperature itself.
The component parts of the boiling curve are as follows:
- The natural convection region AB, where temperature gradients are set up in the pool and heat is removed by natural convection to the free surface and thence by evaporation to the vapor space.
- The onset of nucleate boiling (ONB), where the wall superheat becomes sufficient to cause vapor nucleation at the heating surface. This may occur close to the point where the curves AB and B'C meet, as is usually the case for water at atmospheric pressure and above. Alternatively, it may occur at much larger superheats than those required to support fully developed nucleate boiling, resulting in a sharp drop in surface temperature from B to B' for the case of a constant surface heat flux. This latter behavior is associated with fluids at very low reduced pressures, e.g., water below atmospheric pressure and liquid metals in particular.
- The nucleate boiling region (B'C), where vapor nucleation occurs at the heating surface. Starting with a few individual sites at low heat fluxes, more sites become active as the heat flux is increased. Bubble departure frequency also increases with increasing heat flux. Finally, at high heat fluxes, the vapor structure changes significantly with bubble coalescence leading to formation of vapor patches and columns close to the surface.
- The critical heat flux (CHF or point D) marks the upper limit of nucleate boiling where the interaction of the liquid and vapor streams causes a restriction of the liquid supply to the heating surface.
- The transition boiling region (DE) is characterized by the existence of an unstable vapor blanket over the heating surface that releases large patches of vapor at more or less regular intervals. Intermittent wetting of the surface is believed to occur. This region can be studied only under conditions approximating a constant surface temperature.
- The film boiling region (EF), where a stable vapor film covers the entire heating surface and vapor is released from the film periodically in the form of regularly spaced bubbles. Heat transfer is accomplished principally by conduction and convection through the vapor film, with radiation becoming significant as the surface temperature is increased.
In the natural convection region (1), the liquid may be at or below the saturation temperature. The temperature gradient away from the surface may be established from work on single-phase natural convection (see Section 174). The remaining regions of the boiling curve will now be considered in more detail.
... You need a subscriptionOpen in a new tab. to view the full text of the article. If you already have the subscription, please login here