Navigation by alphabet
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y ZIndex
Plate Fin Surface Geometries
DOI 10.1615/hedhme.a.000298
3.9.3 Plate fin surface geometries
Figure 1 shows typical surface geometries used for heat transfer to gases in compact plate-fin heat exchangers. The figure shows six basic types of surface geometry, and defines the geometric variables associated with each type. By varying the basic geometric variables for each type of surface, it is possible to obtain a wide variety of specific surface geometries. Although typical fin pitches are five to eight fins per centimeter, applications may exist for as many as 1,200 fins per meter in automotive applications. Fin thicknesses of 0.1–0.25 mm are common. Fin heights may range from 0.25 to 2 cm. A plate-fin exchanger with 600 fins per meter provides about 1,300 m2/m3 of heat transfer surface per cubic meter of volume. Such a heat exchanger would contain 10 times as much heat transfer surface per unit volume as in a typical shell-and-tube heat exchanger having 19 mm diameter tubes. Operated at a frontal velocity of 3 m/s, the heat transfer coefficient based on prime surface area would be on the order of 1,800 W/m2 K.

Figure 1 Plate-fin exchanger surface geometries (Webb and Kim, 2005): (a) plain rectangular fins; (b) plain triangular; (c) wavy; (d) offset strip; (e) perforated; (f) louvered
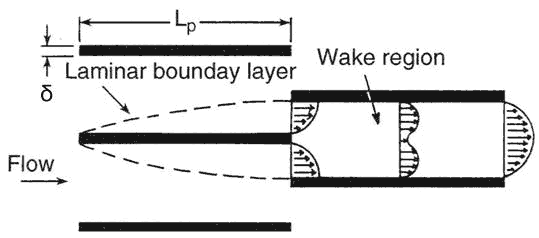
The rectangular and triangular fins are simple, plain fin geometries that offer increased heat transfer because of their small hydraulic radius. The addition of perforations or holes in the fin surface provides some heat transfer increase as a result of wake mixing that occurs in the hole regions. The wavy fins yield increased heat transfer because of secondary flows established by the wavy channel. The offset-strip fin, louvered, and pin fins all provide significant heat transfer augmentation via the repeated growth of laminar boundary layers, followed by dissipation in the wake regions. This boundary layer development and dissipation is illustrated in Figure 2. The offset fin provides heat transfer coefficients two to three times higher than a plain fin geometry having the same fin pitch. The louver fin geometry is typically used in automotive heat exchangers, while the offset-strip fin is typically used in large brazed aluminum heat exchangers for cryogenic applications and in aerospace applications.
... You need a subscriptionOpen in a new tab. to view the full text of the article. If you already have the subscription, please login here