Navigation by alphabet
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y ZIndex
Laminar Flow Surfaces
DOI 10.1615/hedhme.a.000300
3.9.5 Laminar flow in plain surface geometries
It was previously noted that very compact surfaces (small hydraulic diameter) may operate at Reynolds numbers well within the laminar flow region. In the laminar regime, surface geometries designed to produce boundary layer interruptions may be of little benefit. Therefore, plain fin surfaces are likely candidates for very compact designs operating in the laminar regime. Laminar flow plate-fin geometries are also used in rotary regenerators, discussed in Section 3.15. For fully developed laminar flow, Nu and f Re are independent of Reynolds number. But Nu and f Re are dependent on the cross-sectional shape of the flow channel. Because of the small hydraulic diameter of the flow channels, their L /Dh may be sufficiently large that fully developed laminar flow solutions are applicable. For most channel shapes. the mean Nusselt number and friction factor will be within 10% of the fully developed for gases if L /Dh > 0.2 Re.
Table 1 [from Webb and Kim (2005)] gives fully developed laminar flow solutions for 11 channel shapes of interest in compact heat exchanger design. The tables give NuH (constant heat input per unit length with uniform peripheral temperature) and NuT (constant wall temperature). The ratio j /f (for Pr = 0.7) is proportional to the required flow channel frontal area for a specified α A and friction power. The hydraulic entrance length Lhy+ = (X /Dh) /Re is the dimensionless length required for the centerline velocity to attain 99% of its fully developed value. The constant K(∞) defines the pressure drop increment to be added to account for the increased friction in the flow development region. The pressure drop, accounting for the flow development region, is
\[\label{eq1} \Delta p=\left[\frac{4f_{fd}L}{D_{h}}+K(\infty)\right]\frac{G^{2}_{c}}{2\rho} \tag{1}\]
Table 1 Fully developed laminar flow solutions a
| a jH and jT for Pr = 0.7. T ≈ constant temperature. H ≈ heat flux, ≈ heat flux with uniform peripheral temperature. | |||||||
| Geometry | NuH | NuT | f Re | K(∞) | jH /f | jT /f | Lhy+ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
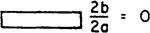 | 8.235 | 7.541 | 24 | 0.686 | 0.386 | 0.354 | 0.0056 |
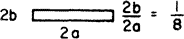 | 6.490 | 5.597 | 20.585 | 0.879 | 0.355 | 0.306 | 0.0094 |
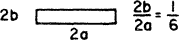 | 6.049 | 5.137 | 19.702 | 0.945 | 0.346 | 0.294 | 0.0110 |
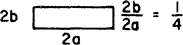 | 5.331 | 4.439 | 18.233 | 1.076 | 0.329 | 0.274 | 0.0147 |
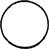 | 4.364 | 3.657 | 16.00 | 1.24 | 0.307 | 0.258 | 0.038 |
 | 4.123 | 3.391 | 15.548 | 1.383 | 0.299 | 0.245 | 0.0255 |
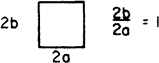 | 3.608 | 3.091 | 14.227 | 1.552 | 0.286 | 0.236 | 0.0324 |
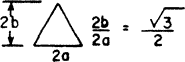 | 3.111 | 2.47 | 13.333 | 1.818 | 0.263 | 0.209 | 0.0398 |
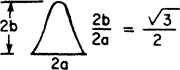 | 3.014 | 2.39 | 12.630 | 1.739 | 0.269 | 0.214 | 0.0408 |
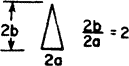 | 2.88 | 2.22 | 13.026 | 1.991 | 0.249 | 0.192 | 0.0443 |
 | 2.60 | 1.99 | 12.622 | 2.236 | 0.232 | 0.178 | 0.0515 |
... You need a subscriptionOpen in a new tab. to view the full text of the article. If you already have the subscription, please login here