Navigation by alphabet
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y ZIndex
Two-Phase Loop with Capillary Pump
DOI 10.1615/hedhme.a.000318
3.10.9 Two-phase loop with capillary pump
Leonid L. Vasiliev, Donatas Mishkinis
A. Introduction
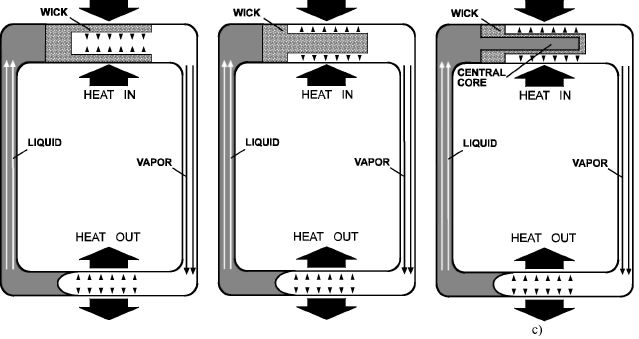
The Two-Phase Loop with Capillary Pump (Figure 1) is a passive heat transfer device and is a form of heat pipe. Phase change take place in the regions of heat input (evaporation) and heat rejection (condensation). Thermal energy is transferred in latent form by vapor and condensed liquid is returned back by action of capillary forces (a unique characteristic of a heat pipe). The distinguishing characteristics of the Two Phase Loop with Capillary Pump are the placement of a capillary structure only in the evaporator and the presence of separated channels for vapor and liquid. There are no counter flows of vapor and liquid as in the classical heat pipes but only unidirectional flows in a closed loop. The separation of the vapor and liquid flows allows a significant reduction of the viscous pressure losses in the shielded (adiabatic) section (smooth wall tubing is usually used as the channels), and the elimination of entrainment of liquid by vapor, in comparison with classical heat pipes. The placement of the capillary pump in the evaporator allows the use of micron-size porous structures, which are capable of developing a very high capillary head. Sintered metal powder capillary pumps manufactured in the Institute of Thermal Physics (Ekaterinburg, Russia) are shown on Figure 2. The normal effective pore radii of such capillary pumps for Two Phase Loops are in the range 0.5–20 microns.
The heat transfer in the evaporator can be organized in two ways: (1) the traditional way, where liquid evaporates from outer wick surface (Philips and Grove, 2003) (Figure 1a) and (2) by evaporation from an "inverted meniscus" where heat and mass flows in the wick have opposite directions (Figure 1b and c). The second approach is used in the great majority of the evaporators in todays Two-Phase Loops with Capillary Pumps. The phenomenon of "inverted meniscus" evaporation was considered in detail by Philips and Grove (2003) and Khrustalev and Faghri (1996). To reduce the wick hydraulic resistance (to minimize the flow path of the of liquid in the porous structure) a central core is usually inserted into the capillary pump (Figure 1c). However, an evaporator without a central core (Figure 1b) also has certain advantages such as preventing undesirable boiling in the wick body and the possibility to design compact flat evaporators for high-pressure working fluids (Philips and Grove, 2003). Due to their specific features, Two-Phase Loops with Capillary Pumps are more flexible and can transfer much higher heat fluxes over much longer distances than classical heat pipes. The Loops are capable of effective operation against gravity (up to several meters) or other body forces [one of the first names for such devices was "anti-gravitational heat pipe" (Philips and Grove, 2003)]. Because the heat pipe is a precursor and close cousin of the Two-Phase Loop with Capillary Pump it is logical to call this class of devices "heat loops" for consistency (Philips and Grove, 2003).
... You need a subscriptionOpen in a new tab. to view the full text of the article. If you already have the subscription, please login here