Navigation by alphabet
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y ZIndex
Properties of Heat Transfer Media
DOI 10.1615/hedhme.a.000538
5.5 PHYSICAL PROPERTY DATA TABLES
5.5.15 Properties of Heat Transfer Media
Hans-Joachim Kilger
A. Introduction
The following tables giving the physical properties of heat tranfser media currently on the market, provide a convenient means of surveying alternative materials. For the most part, these data are drawn from specifications made by the manufacturers. They are consistent with the best knowledge and experience available and are published in good faith, without assessing the respective degrees of their exactness and without any liability accepted, especially with regard to patents in the names of third parties. The trading names are mostly registered trade names.
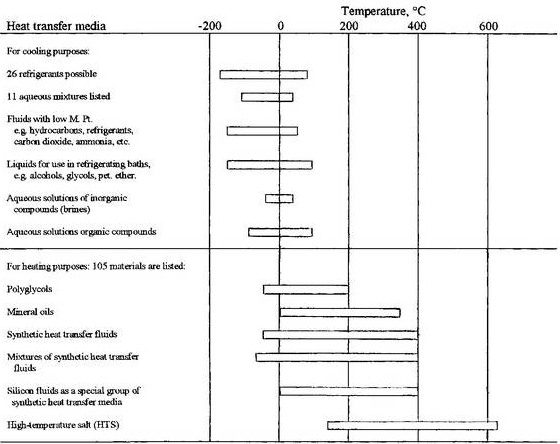
Heat transfer media can be classified according to their ranges of application. There are fluids for heating and fluids for cooling, namely refrigerants. The latter, capable of operation between -100 °C and +150 °C, are dealt with first. Heat transfer media in the more literal sense cover the range between -50 °C and +400 °C. For working temperatures between +142 °C and +620 °C some high-temperature salt (HTS) or other is required. In Figure 1 the respective ranges of application in terms of temperature are shown below.
A heat transfer medium may be present in the solid, liquid, and/or vapor phase, can be used to store heat in a reversible form; and can be circulated within the installation. With multiphase substances, such as mixtures of ice and brine or vapor and liquid, a change of phase wall occur during heat exchange with the surroundings, considerable amounts of enthalpy being exchanged with these surroundings at a temperature held constant.
... You need a subscriptionOpen in a new tab. to view the full text of the article. If you already have the subscription, please login here