Content Map
Computational procedure for the special case of two tube-side passes
DOI 10.1615/hedhme.a.000113
1.6 SHELL-AND-TUBE HEAT EXCHANGERS (CELL METHOD)
1.6.6 Computational procedure for the special case of two tube-side passes
E.S. Gaddis
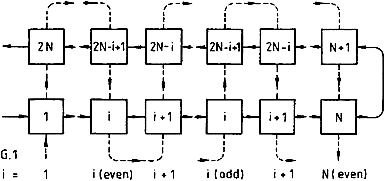
The computational procedure given in this section is presented to enable the user in writing a simple computer code for calculating the effectiveness of a shell-and-tube heat exchanger with two tube-side passes and any number Nb of segmental baffles using the cell method. The corresponding number N of the shell-side passes is (Nb + 1) and the total number of cells is 2N. It is immaterial in this calculation whether the tube-side stream has the lower or the higher heat capacity rate. The procedure is based on the steps explained in Section 112.
A. Heat exchangers with geometry G.1
(a) Case 1: Even number N of shell-side passes
Figure 1 shows the idealized heat exchanger. The procedure of the computations is as follows:
... You need a subscriptionOpen in a new tab. to view the full text of the article. If you already have the subscription, please login here