Content Map
Helical Channels of Rectangular Cross Section
DOI 10.1615/hedhme.a.000182
2.5.15 Helical channels of rectangular cross section
P. Poškas and V. Simonis
A. Introduction
One promising method of enhancing convective heat transfer is to utilise the action of mass centrifugal forces on the flow of the heat transfer agent. This is realized in curvilinear (including helical) channels of different cross sections. Although a good deal of attention has been given to thermohydraulic investigations in curvilinear channels, the results obtained refer primarily to average characteristics, i.e. to the length- and perimeter-averaged mean heat transfer or only to length-averaged parameters. The mean heat transfer in helically coiled tubes of circular cross section is analyzed by Gnielinski in Section 181.
The local heat transfer over the channel length and perimeter has been studied to a much lesser extent. Various studies demonstrate a considerable difference in heat transfer from the separate surfaces of the curvilinear channels.
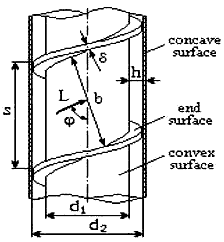
The geometry of the curvilinear channels discussed in the present section is illustrated in Figure 1. The fluid follows a spiral path between an outer tube of diameter d2 (the concave surface) and an inner tube of diameter d1 (the convex surface). The flow is guided into a spiral path by a spiral plate as illustrated.
... You need a subscriptionOpen in a new tab. to view the full text of the article. If you already have the subscription, please login here