Navigation by alphabet
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y ZIndex
Gas Radiation Properties
DOI 10.1615/hedhme.a.000208
2.9 HEAT TRANSFER BY RADIATION
2.9.5 Gas radiation properties
D.K. Edwards
A. The equation of transfer
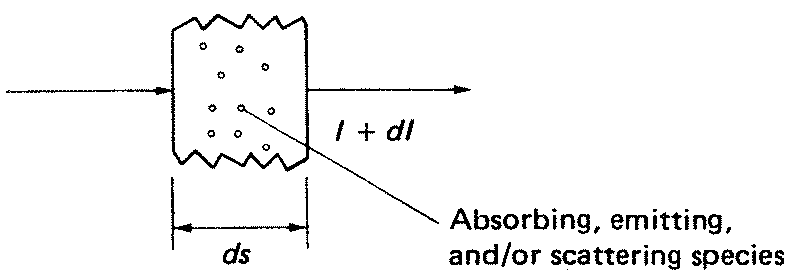
Up to this point, a diathermanous medium has been assumed. In such a medium the radiant intensity I of a stream of photons is unaffected by passage through the medium. More generally, the photons and matter interact. Three processes may be distinguished: (1) net absorption (total absorption minus induced emission), (2) spontaneous emission, and (3) scattering. The latter can be broken down into scattering out of the beam and scattering into the beam. The result is that in slant path increment ds there is an incremental change in intensity dI as pictured in Figure 1. The equation giving dI/ds is named the equation of transfer.
The absorption, emission, and scattering properties of matter are sometimes characterized by cross sections. For example, visualize a spherical oil droplet such as is sprayed into a combustion chamber. The droplet of radius R has a total surface area of 4πR2, but its projected area is πR2. The latter is said to be the geometric cross section. If one examines the shadow behind a droplet that is large compared to the wavelength, one finds, due to diffraction, a shadow area of 2πR2 but a bright halo contains half of the radiant power missing due to the shadow, half of I dΩ 2πR2. Whether the droplet is large or small, the radiant power missing from the incident beam divided by that incident on an area of πR2 is termed the extinction efficiency Qe. Thus if one considers the halo radiation as scattered, that is, caused to deviate in direction, the extinction efficiency of a large particle is 2; but, if one considers the halo as undeviated, a more reasonable view for engineering power transfer calculations, then Qe is 1 for a large particle.
The power missing from the shadow may have been absorbed, or it may have been scattered into other directions. The fraction scattered into other directions is called the albedo for single scatter ωs. The fraction 1 – ωs is sometimes called the particle emissivity. Actually it would be better called the particle absorptivity, but Kirchhoff’s law is invoked. The quantity ωsQe is called the scattering efficiency Qs, and (1 – ωs)Qe is called the absorption efficiency Qa.
... You need a subscriptionOpen in a new tab. to view the full text of the article. If you already have the subscription, please login here