Navigation by alphabet
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O P Q R S T U V W X Y ZIndex
Thermodynamic cycles
DOI 10.1615/hedhme.a.000398
3.26.2 Thermodynamic cycles
J. R. Barbosa Jr. anf C. J. L. Hermes
In addition to identifying the natural direction of energy transfer processes, the Second Law of Thermodynamics states that some forms of energy have higher quality than others. Whereas there are no limits for conversion of high-quality energy (e.g. work) into low-quality energy (e.g. heat), the Second Law imposes theoretical limitations for the conversion of heat into work and for the transfer of heat from a low temperature thermal energy reservoir (source) to a high temperature thermal reservoir (sink).
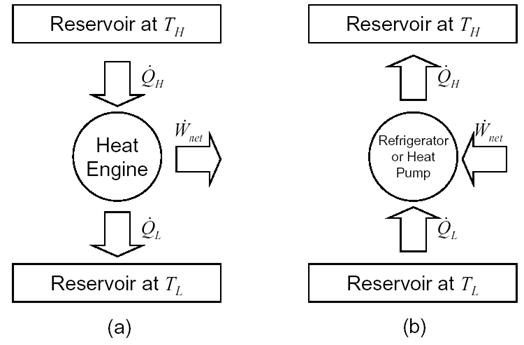
A heat engine, as depicted in Figure 1(a), is a device that operates in a cycle and converts heat into work. The rate of heat input from the high temperature reservoir is Q̇H and part of this heat is converted into work, Ẇnet. For a system undergoing a cycle, the change in internal energy is zero and the rate of heat rejection to the low temperature reservoir is Q̇H = Q̇L – Ẇnet.
The ratio of the net work output to the total heat input to the heat engine represents the efficiency with which it converts heat into work. The thermal efficiency is defined as,
... You need a subscriptionOpen in a new tab. to view the full text of the article. If you already have the subscription, please login here